Art DeFi Journal
Where Digital Art Meets Finance
Each article is enhanced daily to go deeper rather than wider.
Edition August 1, 2025
cover page
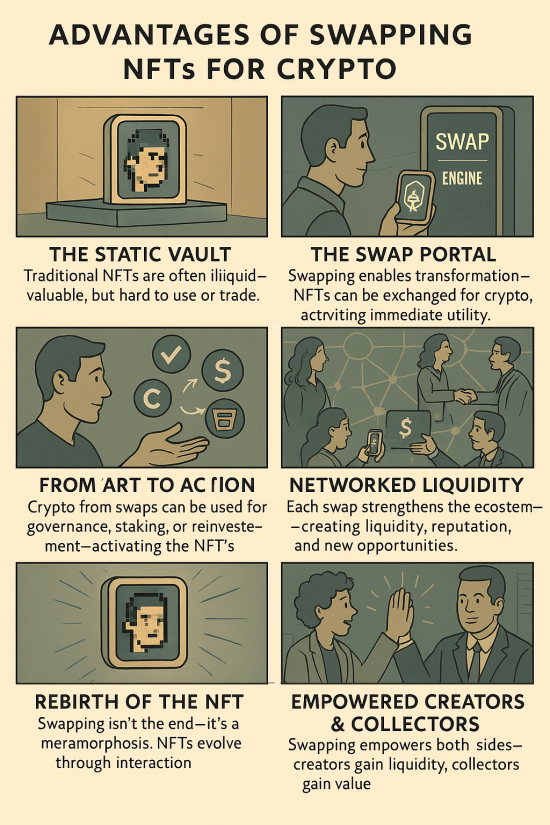
HERE’s A logical, step-by-step process for both buyer and seller wallets during a barter-based NFT exchange on xdaleGallery.com is outlined below. This ensures each party’s wallet, responsibilities, and the direction of XER tokens are clearly distinguished at every step
⁂ Slow Motion NFT Barter Process
Step 1: Discover and Select the NFT
Buyer’s Wallet versus Seller’s Wallet: Step-by-Step.
Buyer: Explores xdaleGallery.com and chooses a desirable NFT (digital artwork) to acquire.paste.txt
Step 2: Set Up a Crypto Wallet
Buyer: Sets up a compatible crypto wallet (e.g., MetaMask, Coinbase Wallet) for holding XER and interacting with the marketplace.paste.txt
Seller: (If not already set up) also needs a crypto wallet compatible with the platform to receive XER and manage NFTs.
Step 3: Register/Log In
- Buyer: Creates an account and logs in to xdaleGallery.com in order to access personalized exchange and asset upload features.paste.txt
- Seller: Must also be registered and logged in to list NFTs and receive XER tokens.
- Step 4: Upload and List Asset (Buyer’s Asset, for Swapping)
- Buyer: Uploads details & proof of ownership for their physical asset (e.g., gold watch) to xdaleGallery.com.
- Platform: Reviews, authenticates, and lists the asset.paste.txt
- Step 5: Asset Valuation and Notification
Platform: Assigns a fiat value to the buyer’s uploaded asset, calculates liquidation and fees, and notifies the buyer of the number of XER tokens they’ll receive net of platform fees.paste.txt
Step 6: Asset Surrender and XER Credit
- Buyer’s Wallet: Upon acceptance, the buyer transfers ownership of their asset to xdaleGallery.com.
- Platform: Liquidates the asset or arranges an onward sale, then credits the buyer’s crypto wallet with the agreed amount of XER tokens (less any fees).paste.txt
- Step 7: Acquire Additional XER Tokens (if required)
- Buyer: If more XER is needed to purchase the NFT, the buyer can buy additional XER tokens using fiat or crypto and deposit them to their wallet.paste.txt
- Step 8: Connect Wallet for Marketplace Transaction
- Buyer: Connects their crypto wallet (now with sufficient XER) to the NFT marketplace interface on xdaleGallery.com.paste.txt
- Seller: Ensures their wallet is capable of receiving XER and transferring NFTs.
- Step 9: Initiate NFT Purchase (Swap)
- Buyer: Selects the NFT, specifies the XER amount, and initiates the purchase/swap.paste.txt
- Smart Contract/Platform: Automates and verifies the transfer of XER from buyer’s wallet to seller’s wallet (or escrow/account if platform-mediated).paste.txt
- Seller’s Wallet: Receives XER tokens equivalent to the sale value once smart contract conditions are met.
- NFT: Is escrowed and then transferred to the buyer’s wallet.
- Step 10: Confirm and Finalize Transaction
- Buyer: Confirms and signs the transfer/purchase in their wallet app, covering network (gas) fees as needed.paste.txt
- Blockchain: Records the NFT/asset ownership transfer and XER payout for audit.
- Step 11: Settlement and Management
- Buyer’s Wallet: Receives the NFT, visible in wallet or on xdaleGallery.com dashboard.
- Seller’s Wallet: XER tokens are now available for them to withdraw or use for further exchanges on the platform.paste.txt
- recap
- Industry: NFT Fine art
- Distribution Method: e-Gallery
- Finance Method: DeFi
- Leveraging NFT barter, a token like XER (xDALE Ethereum Resource) can act as an independent
- intermediary, earning fees by facilitating NFT transactions between artists, collectors, and
- xDALEGALLERY clients.
- XER would execute NFT barter settlements between the artist and xDALEGALLERY using a
- combination of smart contracts, token swaps, and decentralized exchange mechanisms designed for
- flexibility and transparency.
- Settlement Workflow
- Smart Contracts Facilitate Trade
Each NFT barter or swap is initiated through a smart contract that defines the terms: which NFTs or
tokens are being exchanged and any associated fees or royalties.
The smart contract escrows the NFTs and validates both parties’ assets before trade execution,
ensuring neither party can default. - XER as Transaction Medium
XER tokens function as the transactional bridge, enabling the exchange of NFTs for other NFTs,
altcoins, or even stablecoins like USDT.
Example: An artist mints an NFT, and a collector at xDALEGALLERY offers either another NFT or
altcoin. XER tokens are used to mediate and facilitate the swap, potentially covering fees and ensuring
liquidity. - Decentralized Swap and Liquidity
The platform integrates decentralized swap functionality (DALEx), allowing parties to directly convert
XER to stablecoins or altcoins if desired.
XER can pool liquidity, making instant settlements possible and supporting further rounds of trading
outside the original artist-gallery transaction. - Staking, Rewards, and Compliance
NFT contributors may lock XER tokens for added benefits (priority participation, rewards, discounts)
during settlement windows.
All transactions are governed and recorded transparently on-chain to ensure compliance, auditability,
and regulatory safety. - Finalization and Release
Upon conditions being met, the smart contract finalizes the barter, instantly transferring ownership of
NFTs and releasing any XER involved according to the agreed terms.
Additional platform rewards (such as discounts for future mints or staking bonuses) may also be
distributed at this point as incentives for further engagement.
In summary, XER acts as a programmable, liquid intermediary using smart contracts, token-based
liquidity, and decentralized swapping to securely settle NFT barters between artists and
xDALEGALLERY.
Masthead (Placeholders – Replace for Actual Release)
- Editor-in-Chief: [Douglas Crosdale]
- Managing Editor: [Name]
- Art Director: [Name]
- Lead Writer: [Name]
- Community Editor: [Name]
- Contributors: [List]
- Designer: [Name]
- Webmaster: [Name]
- Photography & Media: [Name]
- Research: [Name]
- Publisher: Crosdale, Inc.
- Contact: info@artdefi.com
Cover Image
“DeFi Art Journal-550×344.png” (Placeholder)
Edition: August 1, 2025
Table of Contents
| Section | Page | Edition Date |
|---|---|---|
| Editorial: Deeper, Not Wider | 1 | Aug 1, 2025 |
| Feature: NFTs 2025 – Strategic Comeback | 2 | Aug 1, 2025 |
| Inside XER & Hypsoverse | 4 | Aug 1, 2025 |
| DAO Governance Unpacked | 6 | Aug 1, 2025 |
| Corporate NFT Adoption | 8 | Aug 1, 2025 |
| Artist Interview: Beeple | 10 | Aug 1, 2025 |
| Market Outlook & Trends | 12 | Aug 1, 2025 |
| Technology Update: Robotor | 14 | Jun 1, 2025 |
| Legal & Compliance | 16 | May 1, 2025 |
| Patron Economy & Accounting | 18 | Jul 1, 2025 |
| Community Commentary | 20 | Ongoing |
| Classifieds | 22 | Ongoing |
| Next Edition Previews | 24 | Sep 1, 2025 |
Editorial Spread (Page 1)
Editorial: Deeper, Not Wider
“Each article is enhanced daily to go deeper rather than wider.”
— Editor-in-Chief [Douglas Crosdale]
Feature (Page 2)
NFTs Are Making a Strategic Comeback
- Real-World Asset Tokenization: Physical assets like real estate, art, and commodities become tradeable NFTs.
- Bitcoin NFTs: Minting on Bitcoin adds new security and investor appeal.
- Corporate Adoption: Amazon, Salesforce, Starbucks use NFTs for loyalty and customer engagement.
- Tangibility & Rarity: Perks, memberships, and access replace pure speculation.
Inside XER & Hypsoverse (Page 4)
Integration of NFT Futures
- NFT futures enable liquidity, fractional investing, and speculation in high-value art.
- Hypsoverse.com blends curation with financial markets—trade future value of art in real time.
- Core framework: Tokenized exhibits, futures contracts, fractional ownership.
Example Sidebar:
Platform Highlight:
NFTures—Trade the future value of Bored Apes and CryptoPunks.
DAO Governance Unpacked (Page 6)
Curating via DAO
- Power shifts to community: Curate exhibits, vote on featured futures.
- DAO structure: Smart contracts, governance tokens, treasury management, proposals & voting.
Infographic Module (Replace with placeholder image)
“DAO Workflows in XER Ecosystem”
Corporate NFT Adoption (Page 8)
Corporate Integration Cases
- Amazon, Salesforce, Starbucks: Membership, reward NFTs for long-term retention
- Strategy: Loyalty, personalization, bridging digital and real-world value.
Artist Interview (Page 10)
Beeple: Digital Art & Market Forces
- Everydays: The First 5000 Days – $69M NFT landmark.
- CROSSROADS – $6.6M secondary market dynamic NFT.
- Human One – Hybrid sculpture.
- Commentary & Collaborations: Political, social, and pop culture insights.
Quick Facts
- Featured Projects: Christie’s Auctions
- Collaborators: Louis Vuitton, Nike, Katy Perry
Market Outlook & Trends (Page 12)
Forecasts & Alpha
- Curatorial insights become alpha for predicting NFT & art market trends.
- NFT futures: Democratizing access, enhancing liquidity, blending speculation with curation.
Technology Update (Page 14; June Edition)
Automated Robot Sculptor – Robotor
- Carrara, Italy: Automated robot chisels marble and granite up to 15 feet tall.
- Restoration: Monumental Arch of Palmyra recreated in 5 weeks using 3D scans.
- Statement: “The robot-sculptor is already a reality, but the robot-artist will never exist!”
Patron Economy & Accounting (Page 18; July Edition)
XDALE’s Barter & Exchange Accounting Template
lol I’m
| Date | Tx ID | Listed Item | Received Item | XER Purchased | Market Value | Expenses | Final Rate | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2025-07-01 | XDL-XXXXXX | Gold Watch | Artwork XX | XX XER | $XXXXX | $XX.XX | $XXX.XX | Swap |
All swaps timestamped; market valuation reflects liquidation value.
Community Commentary (Page 20; Ongoing)
Letters, Guest Essays, Announcements
- Dear Ms. ambitious minority retiree…
- How X-ERIES Token (XER) suits your sensibilities and ambitions.
- From: Doug Crosdale, Founder
Next Edition Previews (Page 24; September 2025)
Coming Up
- V-ART Spaces: Virtual exhibitions and real estate solutions.
- Staking Mechanisms: Yield, platform rewards.
- Artbtrage: Asset arbitrage & rollup exploits.
Advertising & Classifieds (Page 22)
- Event Announcements, NFT drops, Art Sales, Calls for Contributors.
Back Cover

Join XDALE’s Art Revolution
: Transact, Patronize, Invest.